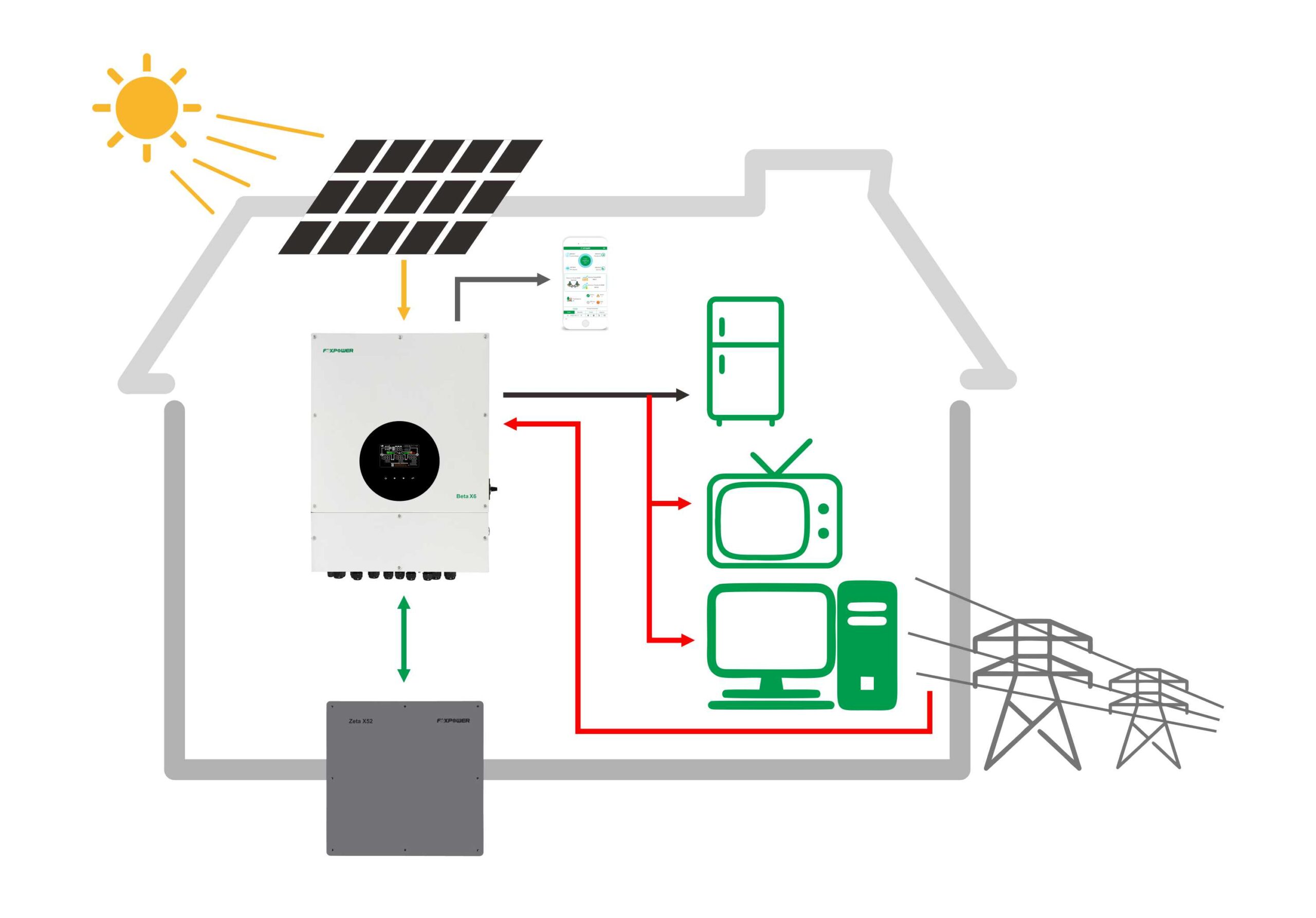
How does photovoltaics work?
Photovoltaic power generation is the process of converting solar radiation into electrical energy using the photovoltaic effect. The photovoltaic effect refers to the excitation of free electrons in a semiconductor material (usually silicon) when light shines on its surface, causing electrons to move inside the material and generate current. Photovoltaic power generation systems typically consist of multiple photovoltaic cells. Each photovoltaic cell is composed of two layers of semiconductor materials: P-type semiconductor and N-type semiconductor. When sunlight shines on the surface of a photovoltaic cell, photons excite electrons near the P-N junction, causing them to transition into the conduction band and generate current. During this process, the electric fields on both sides of the P-N junction push electrons towards the wires of the battery, forming a current. The generated DC current usually needs to be converted into AC power through an inverter for use in the power grid or household electrical equipment. In this way, solar energy is converted into [...]