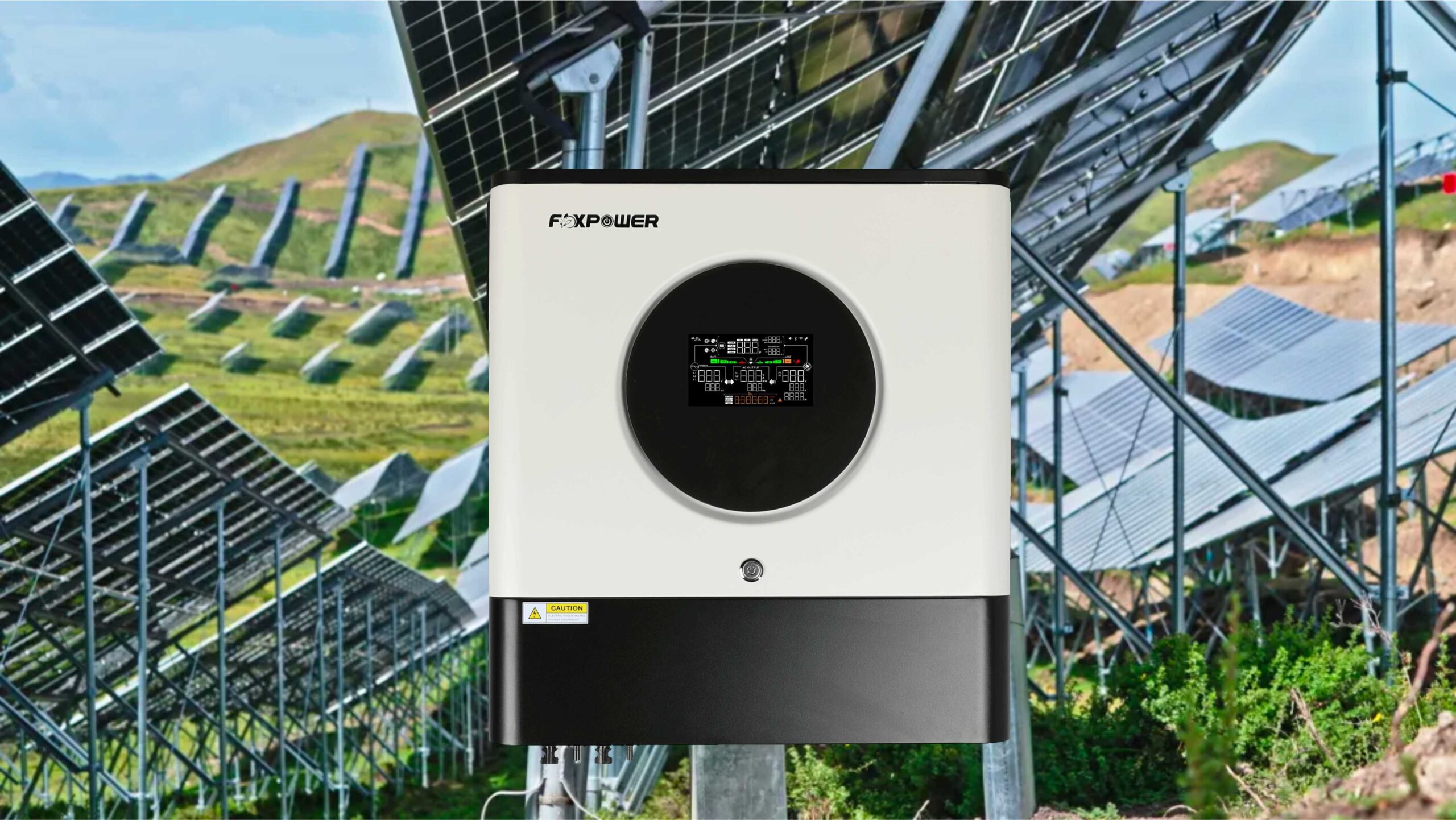
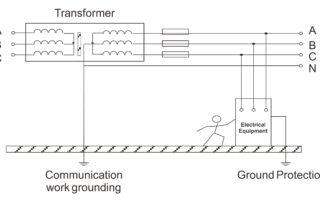
Types and specifications of photovoltaic grounding
In the photovoltaic power station system, grounding design is a crucial part of electrical design, which is related to the safety of equipment and personnel in the power station. Good grounding design can ensure that the power station operates in a safe environment for a long time, reduce the frequency of faults, and improve the overall operational efficiency of the power station. What is grounding? Grounding refers to the connection of the neutral point of the power system and electrical equipment, the exposed conductive parts of electrical equipment, and the conductive parts outside the equipment to the ground through conductors. It can be divided into several types: working grounding, lightning protection grounding, and protective grounding. The function of grounding? Prevent electric shock The impedance of the human body is closely related to the environmental conditions it is in. The more humid the environment, the lower the impedance of the human body, and the more susceptible it is to [...]