Energy storage system is the key support for building a new power system. It can convert electrical energy into chemical energy for storage so that it can be released when needed. At present, air cooling and liquid cooling are the two commonly used heat dissipation methods in energy storage systems.
Different heat dissipation principles
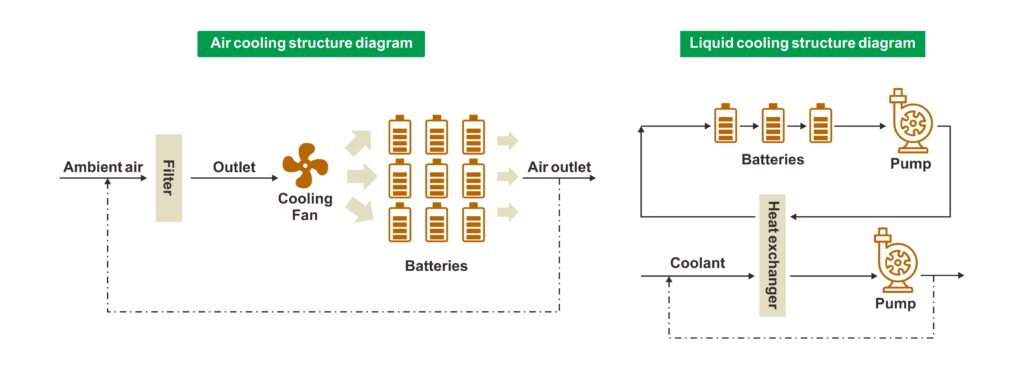
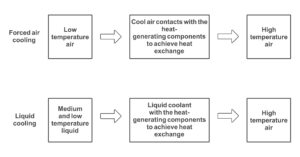
Air cooling is to remove heat through air flow to reduce the surface temperature of the device. The advantages of air cooling are simple structure and low cost, but its heat dissipation effect is greatly affected by factors such as ambient temperature and air circulation, and is not suitable for high-power and high-density equipment.
Liquid cooling is to remove heat through liquid circulation to reduce the internal temperature of the device. The advantages of liquid cooling are good heat dissipation effect and high stability, but its cost is high and it requires maintenance of the liquid circulation system.
Different applicable scenarios
The air cooling system is suitable for energy storage systems of various sizes and types, especially in outdoor environments. It is currently the most widely used cooling technology, such as industrial refrigeration, communication base stations, data centers, temperature control scenarios, etc., with relatively high technical maturity and reliability. Especially in medium and low power scenarios, air cooling is still the mainstream.
The liquid cooling system is also suitable for energy storage systems of various sizes and types, especially large-scale, high-energy-density energy storage projects, where the battery pack has high energy density, fast charging and discharging speed, and the advantages are particularly obvious in occasions with large changes in ambient temperature.
Different design complexity
The design of air-cooled energy storage system is relatively simple, mainly installing cooling fans and air circulation paths. The core of air cooling is air conditioning and air ducts. Air conditioning refrigeration and air ducts exchange heat;
Liquid cooling design is usually more complex, and it is necessary to consider the layout of the liquid circulation system, the selection of pumps, the circulation and maintenance of coolant, etc.
Different heat dissipation effects
The heat dissipation effect of air cooling is greatly affected by factors such as ambient temperature and air circulation, and generally cannot meet the heat dissipation requirements of high-power equipment. Liquid cooling has a better heat dissipation effect, which can effectively reduce the internal temperature of the equipment and improve the stability and life of the equipment.
Different operating power consumption
The composition of power consumption is different. The power consumption of air cooling is mainly air conditioning + electrical compartment fan; the power consumption of liquid cooling is mainly liquid cooling unit + electrical compartment fan (some manufacturers use whole machine liquid cooling). Under the same conditions and maintaining the same temperature, the power consumption of air cooling is higher than that of liquid cooling.
Different costs and maintenance
The cost of air cooling is low and maintenance is simple. However, due to its limited heat dissipation effect, it may be necessary to increase the number of radiators or increase the fan speed to improve the heat dissipation effect, thereby increasing energy consumption and maintenance costs.
The cost of liquid cooling is high and requires maintenance of the liquid circulation system. However, due to its good heat dissipation effect and high stability, it can reduce the failure rate and maintenance cost of the equipment. In the long run, its overall cost may be lower than that of air cooling.
Different noise and space occupancy
The noise of air cooling is low and has less impact on the environment. However, due to the need to install fans and radiators, it may occupy a certain amount of space.
Liquid cooling produces high noise and has a certain impact on the environment. However, due to its small radiator size, it can effectively save space. In addition, liquid cooling can also reduce the impact of noise on the environment by optimizing the radiator design and layout.
Different safety and risk points
Air cooling is safer because of its simple structure and no risk of liquid leakage. However, attention should be paid to the safety of the fan to prevent damage or overheating of the fan.
The safety of liquid cooling is relatively low, and there are risks such as liquid leakage and corrosion. Therefore, the liquid cooling system needs to use high-quality materials and strict sealing design to ensure safe operation.
Summary
Air cooling and liquid cooling are two commonly used heat dissipation methods in energy storage systems, and they each have their own advantages and disadvantages. When choosing a heat dissipation method, it is necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as the actual power of the equipment, heat dissipation requirements, and cost budget. With the development of technology, more efficient and low-cost new heat dissipation methods (such as a combination of air cooling and liquid cooling, immersion, etc.) may appear in the future to provide guarantees for the stable operation of energy storage systems.