In the field of new energy, photovoltaic inverters and energy storage inverters are important devices that play an indispensable role in our lives. But what is the difference between these two? We will conduct in-depth analysis of these two inverters from the aspects of structure, function, and application scenarios.
Structural differences
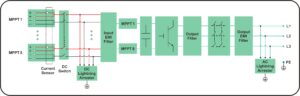
Firstly, in principle, an inverter is mainly a device that converts DC power into AC power. It utilizes the switching characteristics of semiconductor devices such as field-effect transistors or thyristors to control the power supply voltage and current through rapid switching, thereby achieving the conversion of DC to AC power.
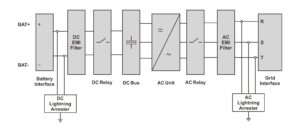
Energy storage inverters (PCS) are a broader concept that involves converting and regulating electrical energy through power electronic devices to achieve power transmission, conversion, and control. PCS mainly includes modules such as rectification, inverter, DC/DC conversion, among which the inverter module is just one of its components.
Functional characteristics
From a functional perspective, photovoltaic inverters mainly focus on converting the direct current generated by solar photovoltaic panels into alternating current for use in power grids or electrical appliances. It optimizes the output power of solar photovoltaic arrays through internal circuits and control modules, processes the DC electricity generated by photovoltaic panels in a series, and finally outputs AC electricity that meets the requirements of the power grid.
Energy storage inverters focus more on bidirectional conversion and intelligent management of electrical energy. It can not only convert direct current into alternating current, but also convert alternating current into direct current for storage. In addition to realizing the conversion from DC to AC, it also supports BMS/EMS linkage, cluster level management, and improves the charging and discharging capacity. It can independently manage peak shaving and valley filling locally, and intelligently schedule the charging and discharging operations of the energy storage system.
Application scenarios
In terms of application scenarios, photovoltaic inverters are mainly used in solar power generation systems, such as household photovoltaic systems, industrial and commercial photovoltaic projects, and large-scale ground power stations. Its main function is to convert the direct current energy of the solar power generation system into alternating current energy and integrate it into the power grid.
Energy storage inverters, on the other hand, are more focused on applications in electrochemical energy storage systems, such as energy storage power stations, centralized or series, industrial and commercial, and household scenarios. In these scenarios, energy storage inverters achieve efficient utilization and storage of renewable energy through intelligent management of charging and discharging processes, providing stable and reliable power support for various application scenarios.
Common points and differences
In terms of commonalities, both are power electronic devices used for the conversion and regulation of electrical energy to achieve stable operation of the power system. They all need to meet certain electrical safety standards to ensure the safe operation of the equipment.
In addition, due to the need for an integrated battery management system, the cost of energy storage inverters is relatively high. The function of photovoltaic inverters is relatively single, so the cost is usually lower. At the same time, energy storage inverters also have higher safety requirements. In addition to meeting basic electrical safety standards, the safety of battery management systems and protective measures in the event of battery failure need to be considered.
Summary
In summary, there are significant differences between photovoltaic inverters and energy storage inverters in terms of principles, application scenarios, power output, cost, and safety. In practical applications, suitable equipment should be selected based on specific needs and scenarios.